EventBus是Android开发中常用的通知事件框架,使用EventBus非常简单只需3布即可,那么实际上EventBus是怎么实现订阅通知的?下面我们从源码开始分析
二、源码分析 我们使用EventBus时,需要在生命周期中注册为订阅者 ,代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Override public void onStart () { super .onStart(); EventBus.getDefault().register(this ); } @Override public void onStop () { super .onStop(); EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this ); }
那么我们就从这里开始分析
2.1 EventBus.getDefault() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public static EventBus getDefault () { if (defaultInstance == null ) { synchronized (EventBus.class) { if (defaultInstance == null ) { defaultInstance = new EventBus (); } } } return defaultInstance; }
EventBus.getDefault()是使用单例模式,获取一个EventBus的实例
2.2EventBus.getDefault().register(this) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public void register (Object subscriber) { Class<?> subscriberClass = subscriber.getClass(); List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = subscriberMethodFinder.findSubscriberMethods(subscriberClass); synchronized (this ) { for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : subscriberMethods) { subscribe(subscriber, subscriberMethod); } } }
可以看到重要的方法为
List subscriberMethods = subscriberMethodFinder.findSubscriberMethods(subscriberClass);
2.3 findSubscriberMethods 根据他的名字,猜测是获取相关的订阅者,并返回列表集合
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 List<SubscriberMethod> findSubscriberMethods (Class<?> subscriberClass) { List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = METHOD_CACHE.get(subscriberClass); if (subscriberMethods != null ) { return subscriberMethods; } if (ignoreGeneratedIndex) { subscriberMethods = findUsingReflection(subscriberClass); } else { subscriberMethods = findUsingInfo(subscriberClass); } if (subscriberMethods.isEmpty()) { throw new EventBusException ("Subscriber " + subscriberClass + " and its super classes have no public methods with the @Subscribe annotation" ); } else { METHOD_CACHE.put(subscriberClass, subscriberMethods); return subscriberMethods; } }
获取订阅者的步骤为
1.检查缓存,若缓存存在,则直接返回
2.根据配置参数,使用反射或SubscriberInfo获取,默认情况下不使用反射,减少反射消耗,提高运行效率。
2.4 findUsingReflection,prepareFindState 下面看看反射方法如何获取订阅者信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 private List<SubscriberMethod> findUsingReflection (Class<?> subscriberClass) { FindState findState = prepareFindState(); findState.initForSubscriber(subscriberClass); while (findState.clazz != null ) { findUsingReflectionInSingleClass(findState); findState.moveToSuperclass(); } return getMethodsAndRelease(findState); }
在查找订阅者之前,先做了FindState的准备工作,那先看看prepareFindState()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 private FindState prepareFindState () { synchronized (FIND_STATE_POOL) { for (int i = 0 ; i < POOL_SIZE; i++) { FindState state = FIND_STATE_POOL[i]; if (state != null ) { FIND_STATE_POOL[i] = null ; return state; } } } return new FindState (); }
prepareFindState()主要做了两步操作,1初始化FIND_STATE_POOL为null ,2返回一个FindState对象(FindState用来保存和校验订阅方法)
1 2 3 4 5 void initForSubscriber (Class<?> subscriberClass) { this .subscriberClass = clazz = subscriberClass; skipSuperClasses = false ; subscriberInfo = null ; }
赋值subscriberClass,clazz并设subscriberInfo为null
最后看看获取订阅方法的最主要的方法findUsingReflectionInSingleClass
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 private void findUsingReflectionInSingleClass (FindState findState) { Method[] methods; try { methods = findState.clazz.getDeclaredMethods(); } catch (Throwable th) { methods = findState.clazz.getMethods(); findState.skipSuperClasses = true ; } for (Method method : methods) { int modifiers = method.getModifiers(); if ((modifiers & Modifier.PUBLIC) != 0 && (modifiers & MODIFIERS_IGNORE) == 0 ) { Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes(); if (parameterTypes.length == 1 ) { Subscribe subscribeAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(Subscribe.class); if (subscribeAnnotation != null ) { Class<?> eventType = parameterTypes[0 ]; if (findState.checkAdd(method, eventType)) { ThreadMode threadMode = subscribeAnnotation.threadMode(); findState.subscriberMethods.add(new SubscriberMethod (method, eventType, threadMode, subscribeAnnotation.priority(), subscribeAnnotation.sticky())); } } } else if (strictMethodVerification && method.isAnnotationPresent(Subscribe.class)) { String methodName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName(); throw new EventBusException ("@Subscribe method " + methodName + "must have exactly 1 parameter but has " + parameterTypes.length); } } else if (strictMethodVerification && method.isAnnotationPresent(Subscribe.class)) { String methodName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName(); throw new EventBusException (methodName + " is a illegal @Subscribe method: must be public, non-static, and non-abstract" ); } } }
到这里所有的订阅类的订阅方法已经被保存通过 List subscriberMethods = subscriberMethodFinder.findSubscriberMethods(subscriberClass); 返回
2.5 subscribe(subscriber, subscriberMethod); 最后回到刚开始的register方法,看看subscribe的实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 private void subscribe (Object subscriber, SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod) { Class<?> eventType = subscriberMethod.eventType; Subscription newSubscription = new Subscription (subscriber, subscriberMethod); CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventType); if (subscriptions == null ) { subscriptions = new CopyOnWriteArrayList <>(); subscriptionsByEventType.put(eventType, subscriptions); } else { if (subscriptions.contains(newSubscription)) { throw new EventBusException ("Subscriber " + subscriber.getClass() + " already registered to event " + eventType); } } int size = subscriptions.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i <= size; i++) { if (i == size || subscriberMethod.priority > subscriptions.get(i).subscriberMethod.priority) { subscriptions.add(i, newSubscription); break ; } } List<Class<?>> subscribedEvents = typesBySubscriber.get(subscriber); if (subscribedEvents == null ) { subscribedEvents = new ArrayList <>(); typesBySubscriber.put(subscriber, subscribedEvents); } subscribedEvents.add(eventType); if (subscriberMethod.sticky) { if (eventInheritance) { Set<Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object>> entries = stickyEvents.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> entry : entries) { Class<?> candidateEventType = entry.getKey(); if (eventType.isAssignableFrom(candidateEventType)) { Object stickyEvent = entry.getValue(); checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent); } } } else { Object stickyEvent = stickyEvents.get(eventType); checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent); } } }
主要做的事情为 subscriptionsByEventType用于维护事件(eventType)与订阅者(subscriptions)关系,
typesBySubscriber 用于维护 subscriber(订阅者) 与subscribedEvents(订阅事件)的关系,最后发送事件,发送事件与post类似,这个我们下面再看
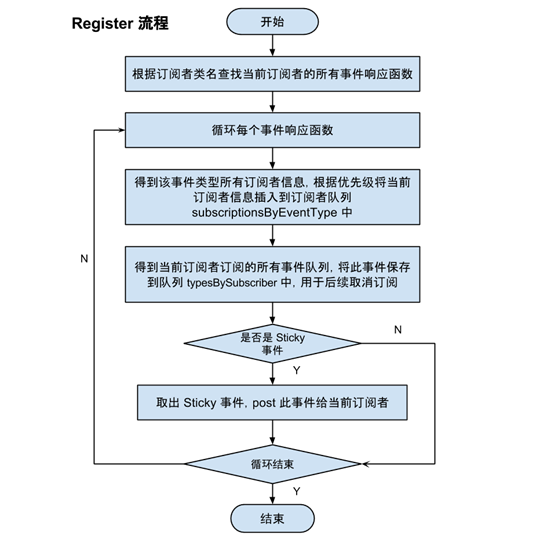
用一张流程图总结一下注册的内容
2.6发布 发送事件给Eventbus
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public void post (Object event) { PostingThreadState postingState = currentPostingThreadState.get(); List<Object> eventQueue = postingState.eventQueue; eventQueue.add(event); if (!postingState.isPosting) { postingState.isMainThread = Looper.getMainLooper() == Looper.myLooper(); postingState.isPosting = true ; if (postingState.canceled) { throw new EventBusException ("Internal error. Abort state was not reset" ); } try { while (!eventQueue.isEmpty()) { postSingleEvent(eventQueue.remove(0 ), postingState); } } finally { postingState.isPosting = false ; postingState.isMainThread = false ; } } }
最终调用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 private void postToSubscription (Subscription subscription, Object event, boolean isMainThread) { switch (subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode) { case POSTING: invokeSubscriber(subscription, event); break ; case MAIN: if (isMainThread) { invokeSubscriber(subscription, event); } else { mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event); } break ; case BACKGROUND: if (isMainThread) { backgroundPoster.enqueue(subscription, event); } else { invokeSubscriber(subscription, event); } break ; case ASYNC: asyncPoster.enqueue(subscription, event); break ; default : throw new IllegalStateException ("Unknown thread mode: " + subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode); } } void invokeSubscriber (Subscription subscription, Object event) { try { subscription.subscriberMethod.method.invoke(subscription.subscriber, event); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { handleSubscriberException(subscription, event, e.getCause()); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { throw new IllegalStateException ("Unexpected exception" , e); } }
最终使用反射,调用订阅者的事件方法。
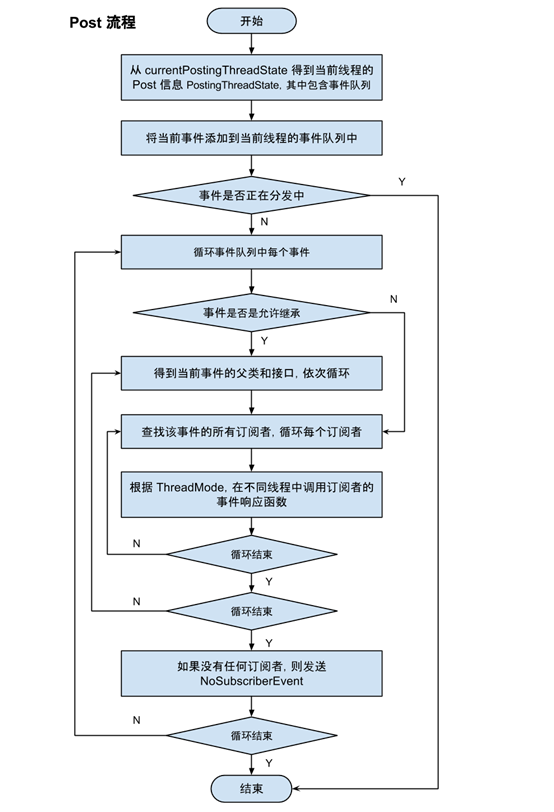
用一张流程图总结下发送流程
以上为EventBus的源码分析,当然还有很多地方没有分析到的,如果有不对的地方欢迎指出。
参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/fuyaozhishang/p/9944653.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/6da03454f75a
全文完。